Progress Report
Emission Reductions
Annual Nitrogen Oxides Figures
Source: EPA, 2019
Last updated: 12/2019
Related Figures
Highlights
Overall Results
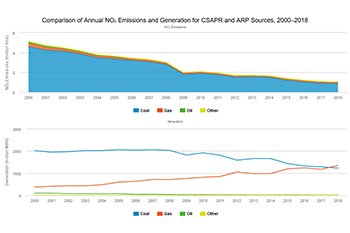
- Annual NOₓ emissions have declined dramatically under the ARP, CAIR, and CSAPR programs, with the majority of reductions coming from coal-fired units. These reductions have occurred while electricity generation has remained relatively stable since 2000.
- These emission reductions are a result of an overall increase in the environmental efficiency at affected sources as power generators installed controls, ran their controls year-round, switched to lower emitting fuels, or otherwise reduced their NOₓ emissions. These trends are discussed further in Chapter 1.
- Other programs – such as regional and state NOₓ emission control programs – also contributed significantly to the annual NOₓ emission reductions achieved by sources in 2018.
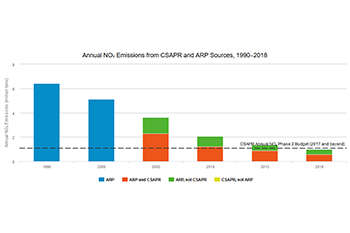
Annual NOₓ Emissions Trends
- ARP: Units in the ARP NOₓ program emitted 1.0 million tons of NOₓ emissions in 2018. Sources reduced emissions by 7.1 million tons from the projected level in 2000 without the ARP, over three times the program’s NOₓ emission reduction objective.
- CSAPR and ARP: In 2018, the fourth year of operation of the CSAPR NOₓ annual program, sources in both the CSAPR NOₓ annual program and the ARP together emitted 1.0 million tons, a reduction of 5.4 million tons (84 percent reduction) from 1990 levels, 4.1 million tons (80 percent reduction) from 2000, and 2.6 million tons (72 percent reduction) from 2005 levels.
- CSAPR: Emissions from the CSAPR NOₓ annual program sources were 590,000 tons in 2018. This is about 1.6 million tons (73 percent) lower than in 2005 and 479,000 tons (45 percent) below the CSAPR NOₓ annual program's 2018 regional budget of 1,069,256 tons.
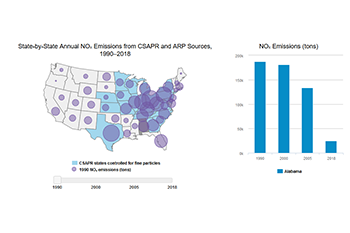
Annual NOₓ State-by-State Emissions
- CSAPR and ARP: From 1990 to 2018, annual NOₓ emissions in the ARP and the CSAPR NOₓ program dropped in 47 states plus Washington, D.C. by a total of approximately 5.4 million tons. In contrast, annual emissions increased in one state (Idaho) by 200 tons from 1990 to 2018.
- CSAPR: Twenty-one states had emissions below their CSAPR 2018 allowance budgets, collectively by 481,000 tons. A single state (Missouri) exceeded its 2018 budget by 1,650 tons.
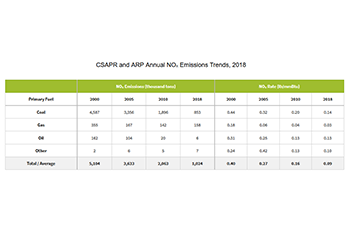
Annual NOₓ Emission Rates
- In 2018, the ARP and CSAPR average annual NOₓ emission rate was 0.09 lb/mmBtu, a 67 percent reduction from 2005.
- Emissions have decreased dramatically since 2005, due in large part to greater use of control technology, primarily on coal-fired units, and increased generation at natural gas-fired units that emit less NOₓ emissions than coal-fired units.
Background Information
Nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) are made up of a group of highly reactive gases that are emitted from power plants and motor vehicles, as well as other sources. NOₓ emissions contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and fine particle pollution, which cause a variety of adverse health effects.