Progress Report
Air Quality
The Acid Rain Program (ARP) and Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) were designed to reduce sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) emissions from power plants. These pollutants contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter, which cause a range of serious health effects and degrade visibility in many American cities and scenic areas, including National Parks. The dramatic emission reductions achieved under these programs have improved air quality and delivered significant human health and ecological benefits across the United States.
To evaluate the impact of emission reductions on air quality, scientists and policymakers use data collected from long-term national air quality monitoring networks. These networks provide information on a variety of indicators useful for tracking and understanding temporal trends in regional air quality.
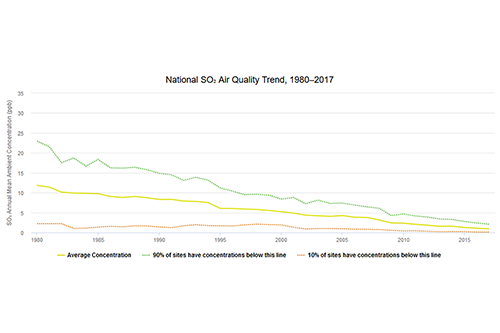
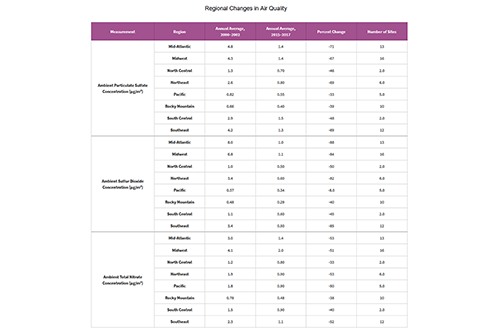
Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxides Trends Figures
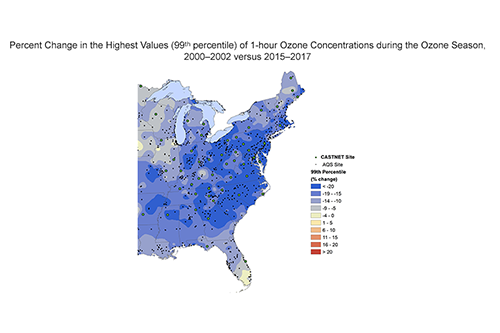
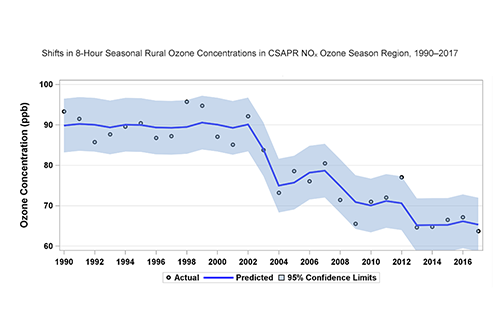
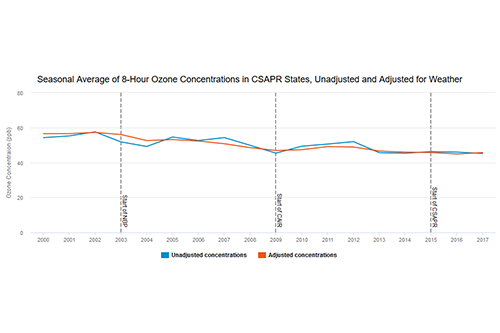
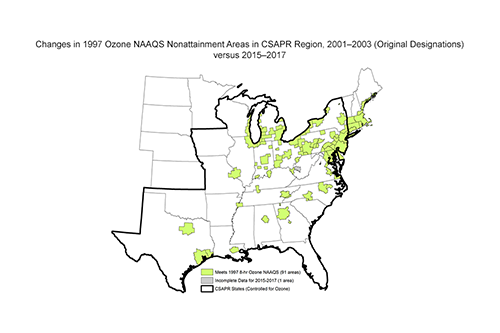
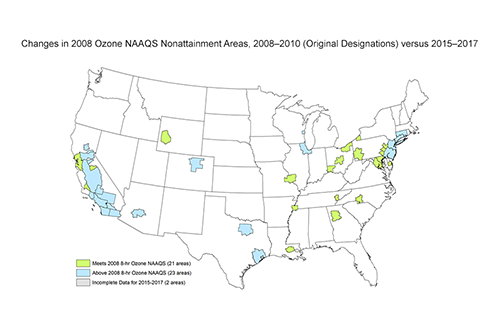
Ozone Figures
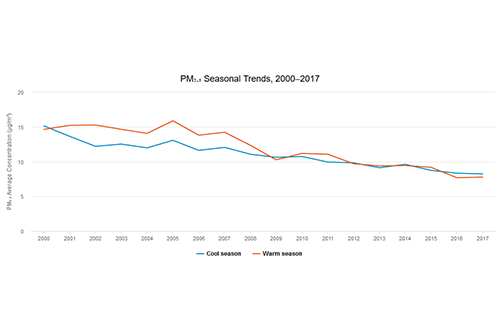
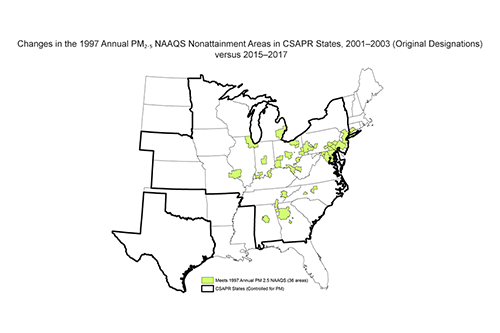
Particulate Matter Figures