Progress Report
Program Basics
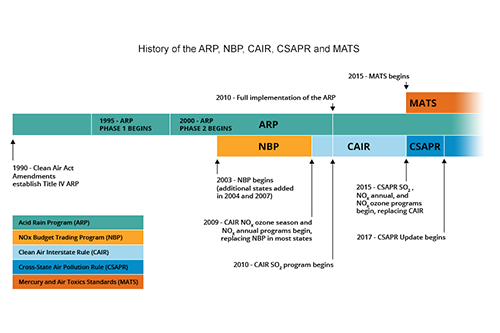
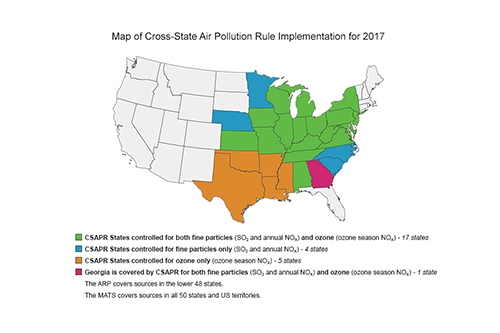
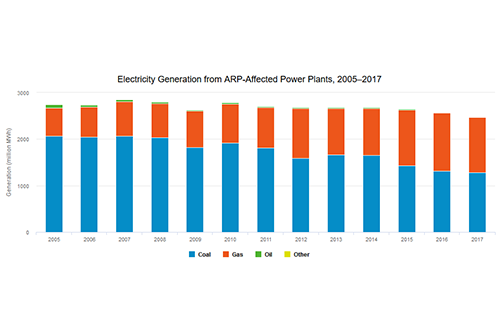
The Acid Rain Program (ARP), the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR), and the CSAPR Update are implemented through cap and trade programs designed to reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) from covered power plants. Established under Title IV of the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments, the Acid Rain Program was a landmark nationwide cap and trade program, with a goal of reducing the emissions that cause acid rain. The undisputed success of the program in achieving significant emission reductions in a cost-effective manner led to the application of the market-based cap and trade tool for other regional environmental problems, namely interstate air pollution transport, or pollution from upwind emission sources that impacts air quality in downwind areas. The interstate transport of pollution can make it difficult for downwind states to meet health-based air quality standards for regional pollutants, particularly PM₂.₅ and ozone. EPA first employed trading to address regional criteria pollution in the NOₓ Budget Trading Program (NBP), which helped northeastern states address the interstate transport of NOₓ emissions causing ozone pollution in northeastern states. Next, NBP was effectively replaced by the ozone season NOₓ program under the Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR), which required further summertime NOₓ emission reductions from the power sector, and also required annual reductions of NOₓ and SO₂ to address PM₂.₅ transport. In response to a court decision on CAIR, CSAPR replaced CAIR beginning in 2015 and continued to reduce annual SO₂ and NOₓ emissions, as well as seasonal NOₓ emissions, to facilitate attainment of the fine particle and ozone NAAQS. Most recently, implementation of CSAPR Update began in 2017. CSAPR Update further reduces seasonal NOₓ emissions to help states attain and maintain a newer ozone National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS).
The Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) set limits on emissions of hazardous air pollutants from covered power plants. EPA published the final standards in February 2012, and the compliance requirements generally went into effect in April 2015. with extensions for some plants until April 2016 and a small number until April 2017. As such, 2017 is the first full year for which the vast majority of sources covered by MATS have reported emissions data to the EPA.
Program Basics Figures