Assessing Outdoor Air Near Schools
Temple Elementary - Diboll, TX
- Understanding the Monitoring Data
- Initial Sampling
- Initial Analysis
- Análisis
- Additional Sampling
- Final Analysis
Results and Analysis of EPA’s Additional Monitoring
EPA selected this school for monitoring because it is located near a lumber, fiberboard and particleboard manufacturing complex which is a source of air toxics emissions. Computer models were used to determine which air toxics may be present at elevated levels in the outdoor air near the school. These models showed that acrolein could be present in the air around the school and prompted EPA to test to see if the levels present may be of concern. Air monitoring was initially conducted at Temple Elementary School from October 28, 2009 to March 8, 2010 to assess concentrations of acrolein and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the air. As provided in the first technical report, EPA was not able to use the acrolein data due to concerns about the consistency and reliability of monitoring results of acrolein. Since the original monitoring, EPA identified several steps that we believe significantly improved the accuracy of acrolein sampling and that provided data that will allow us to understand whether acrolein in the outdoor air poses a health concern at the location of this school. Additional monitoring for acrolein and VOCs was conducted at the original school location from October 31, 2011 to December 13, 2011. Due to reasons unrelated to this monitoring, the school was recently moved two miles northeast of the manufacturing complex.
| Primary Findings | Measured values of acrolein and other VOCs indicate no influence of the source at the original Temple Elementary School location. Concentrations of acrolein and VOCs are similar to those typically measured in most locations throughout the United States and within the range of estimated levels without appreciable risk of adverse effects. |
| Key Pollutants Monitored | Acrolein. Exposure to high levels can cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. |
| Next Steps | Based on the analysis described here, EPA will not extend air toxics monitoring at this location. EPA remains concerned about emissions from sources of air toxics and continues to work to reduce those emissions across the country, through national rules and by providing information and suggestions to assist with reductions in local areas. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) will continue to oversee industrial facilities in the area through clean air regulatory programs. TCEQ has developed air monitoring comparison values for acrolein and many other air toxics pollutants which can be found at http://www.tceq.texas.gov/toxicology/AirToxics.html. |
Summary of Study Approach and Findings
Approach:
- A monitor collected air samples from October 31, 2011 through December 13, 2011 at the Temple Elementary School in Diboll, TX.
- Individual air sample results are posted on this website.
- When the monitoring was complete, we analyzed the results to see if there was a concern from long-term concentrations over a lifetime).
- Also, when the monitoring was complete, we evaluated all the air samples from the on-site monitor. We also evaluated information on wind speed and wind direction from a weather monitor at the school, along with historical weather information and information about nearby sources of acrolein emissions.
Findings:
- Measured values of acrolein and other VOCs indicate no influence of the source at the original Temple Elementary School location. Concentrations of acrolein and VOCs are similar to those typically measured in most locations throughout the United States and within the range of estimated levels without appreciable risk of adverse effects.
- Monitoring data from both sampling events indicate low levels of other VOCs monitored, with longer-term concentration estimates below their comparison levels.
- Acrolein emissions from the key source have decreased from the 13 tons reported in 2002, which was what was modeled by the NATA 2002, to the most recent reports from the manufacturing complex of 4 tons per year.
- EPA has identified several simple steps that we believe have significantly improved the accuracy of acrolein sampling. EPA plans to further improve the method for measuring acrolein.
- Click here for additional information
How We Analyzed the Information We Collected at this School
The analysis considered whether the information collected at the school might raise concerns for the health of children or adults at the school. We looked at the following types of information:
- Measured concentrations and information on acrolein
- Measured wind direction and wind speed at the school
- Information about nearby sources of acrolein emissions
Analysis of Measured Acrolein Concentrations:
1. Compare results with individual sample screening levels: We compared the acrolein measurements with individual sample screening levels which are based on consideration of exposure all day, every day over a period ranging up to at least a couple of weeks , and longer for some pollutants.
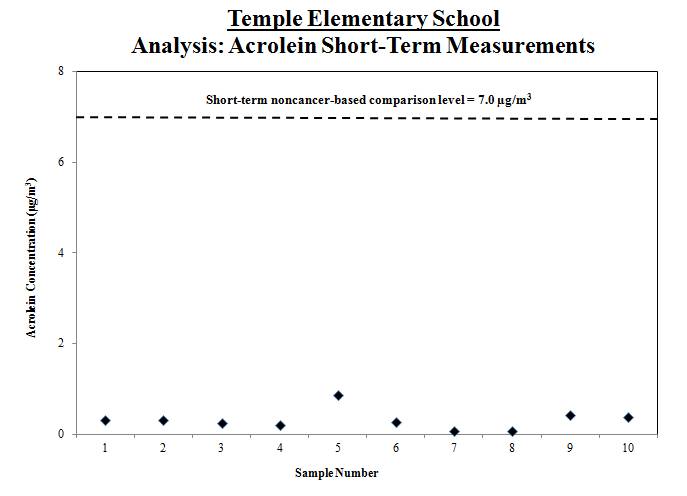
2. Calculate a range: To account for varying air concentrations of acrolein, we calculated a range around the average by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. The longer-term concentration estimate for acrolein was compared to the SAT noncancer-based comparison level and a more recent and relevant comparable level derived by the California EPA.
Result: Concentrations are similar to those typically measured in most locations throughout the United States and within the range of estimated levels without appreciable risk of adverse effects.

Analysis of Measured Wind Direction and Wind Speed at the School
We took measurements of wind direction and speed every day during the sample period. We took special note of the wind speed and direction on the days we took measurements.
| What we looked at | What we found |
| We looked at whether the wind data taken on the days we took measurements of are similar or different from the wind patterns during the entire sampling period. | We found the wind patterns taken on the days we took measurements to be similar to those observed during the entire sampling period. |
| We looked at whether the wind pattern during the sampling period is reflective of regional wind pattern over the long term. | We lack long-term wind data at the monitoring site, and the wind patterns at the NWS station during the sampling period are not similar to the historical long-term wind flow pattern at that location. Wind Patterns across the air monitoring days appear to be more frequently from the source than those observed over the nine year composite period of the nearest NWS. |
Analysis of Information on Nearby Source of Acrolein Emissions
| What we looked at | What we found |
| Whether we could determine if the source was operating as usual during the sampling period | Acrolein emissions from the source have decreased since the 2002 estimate of 13 tons per year used in modeling analyses for this area. The 2011 emissions are approximately 4.0 tons per year. |
| The nearby source of acrolein has a Title V operating air permit issued by TCEQ that includes operating requirements. |
Additional Information
Technical Report for School: Assessing Outdoor Air Near Schools: Additional Monitoring at Temple Elementary School (Diboll, TX) (PDF) (16pp, 180k). The technical report is a follow-up to the original monitoring which took place. The report is geared toward risk assessors, risk managers, and other regulatory agencies.
Background on School Monitoring Effort