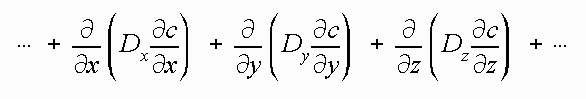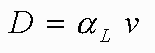EPA On-line Tools for Site Assessment Calculation
Dispersion
Apparent mixing or dilution of solute plumes lead to the inclusion of the dispersion term in the transport equation.
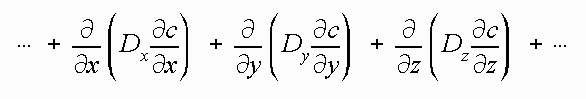
It was recognized that the dilution depended upon
- the seepage velocity (v), and
- the aquifer
The aquifer's role in dilution was viewed as a property of the aquifer, called the dispersivity (a). In the equation, then dispersion (D) is assumed to be
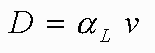
All would have been fine, except that due to heterogeneity the dispersivity of an aquifer is not a constant but is scale dependent. In other words the larger the scale of the problem the higher the dispersivity. This happens because what really is causing most of the dilution in aquifers with flowing ground water is that the solutes encounter different heterogeneities as they go differing distances in aquifers. Thus the velocity changes in different parts of the aquifer and the solutes experience more of these changes as they travel further.