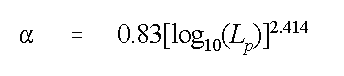Plume Length for Steady One-Dimensional Transport
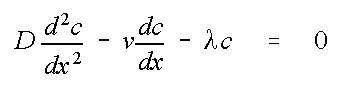
c = concentration [m/L
-3
]
t = time [T]
x = distance [L]
D = dispersion constant [L
2
/T]
v = seepage velocity [L/T]
λ = first order decay constant [1/T]
with the initial and boundary conditions
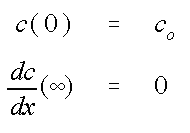
Has the solution (rearranged for length, x):
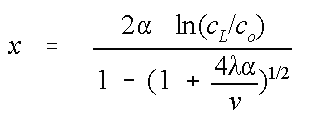
where the dispersion coeffeicient D, has been separated into a dispersivity, α and the seepage velocity v, and
c
L
is the concentration that defines the plume length.
i.e., to find the distance (plume length) to the 0.02 mg/L contour, c
L
is set to 0.02.
Allowing for the dispersivity to be a function of x, f(x):
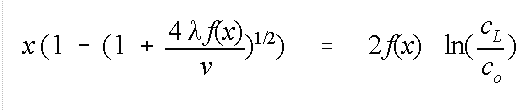
The calculator has three options for f(x):
- Fixed Dispersivity
- One-tenth the plume Length
- Xu and Eckstien (1995) regression relation for plume length (L
p
= x):